 Institute of Applied and Computational Mathematics
IACM is one of the few research institutes in Europe dedicated to promoting the use of advanced mathematics in natural sciences and engineering
Institute of Applied and Computational Mathematics
IACM is one of the few research institutes in Europe dedicated to promoting the use of advanced mathematics in natural sciences and engineering
Spatial Analysis
Geographic Information Systems & Remote Sensing.
ABOUT
The research in the Spatial analysis, Geographic Information Systems and Remote Sensing (SAGISRS) group concentrates on the development of mathematical, statistical and computational tools and methods for generating, analyzing, managing and visualizing geographic (spatial) data. This is a rapidly developing research area often referred to as, Geoinformatics and/or Geotechnology with multiple applications in urban and regional analysis, environmental analysis, climatology, urban climate and air quality, etc.
The tools and methods the group develops are useful for public and private organizations to analyze spatial information and formulate rational economic development, social and environmental policies and evaluate alternative mitigation plans. Specifically, the group develops:
- Spatial decision support systems using Geographic Information Systems (GIS) methodologies and mathematical models simulating various environmental and urban processes,
- Remote sensing methodologies for: extracting geo-information products and indicators from satellite observations; adjusting machine learning algorithms to estimate sub-pixel fractions; downscaling bio-geophysical parameters derived from satellites synergies; analyzing long time series of satellite images (Big Data) in cloud computing environment; and analyzing UAV hyperspectral and thermal imagery,
- Urban climate methods to analyze urban form and function, by combining satellite derived surface parameters with in-situ observations of urban heat fluxes and CO2 emissions from micrometeorological towers (Eddy Covariance and Net Radiation equipment) and standard meteorological and air quality variables from Wireless Sensors Networks.
- Methodologies for the analysis of the organization of urban areas with respect the distribution of the land uses and the built-up densities, the socio-economic characteristics of the population, the traffic patterns in the street network etc.
- Tools for the visualization and management of digital maps on the web.
Group members include researchers with a wide spectrum of expertise from quantitative geography, remote sensing, statistics, applied informatics, atmospheric physics and urban and regional planning. The research effort has been supported from grants from competitive EU projects and grants from Greek public organizations. EU research programs the group has participated include H2020, INTERREG, ERA.Net, FP7, LIFE, ESA and many others. Funding has been also obtained from the General Secretariat of Research and Technology of Greece (GSRT), the Hellenic Statistical Authority, the Region of Crete, the Athens Urban Transport Organization, the Ministry of Health, The Municipality of Heraklion and others.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT ACTIVITIES
Urban Analysis: In the last fifty years urban areas worldwide are growing rapidly. Concentration of people leads to easy connectivity, economies of scale and higher productivity, increased buildup densities and changes in lifestyles, it has however, adverse impacts on the environment. Some of the urban analysis research topics studied in the group include:
- The distribution of land uses and buildup densities to identify urban form and sprawl characteristics,
- Social area analysis, that is the analysis of the socio-economic characteristics of the population to identify neighborhoods with common characteristics, the location of segments of the population in need, etc.,
- Urban growth models,
- Urban metabolism and the way it affects consumption of various resources,
- Urban climate research focusing on: analyzing satellite and UAV observations to derive urban surface morphology, cover and fabric; identifying Local Climate Zones, developing footprint models to deal with urban surface anisotropy; monitoring urban energy balance; analyzing urban heat island, thermal comfort and energy efficiency; analyzing Eddy Covariance observation to estimate CO2 emissions and adjusting methods for pollutants dispersion in the urban boundary layer.
- The concentration of air particles in urban areas,
- The analysis of traffic patterns in the street networks of urban areas

Spatial decision support system: SDSS are information systems for supporting decision making and have extensive applications in environmental planning, resources allocation, business decision making and other fields. Through an integrated and user-friendly environment, they bring together simulation models, GIS databases, impact assessment methodologies and decision rules. The research of the group concentrates on the integration of simulation models with the GIS systems, the development of various spatial datasets and the design of the end user interface. Application areas studied in the group include:
- Simulation of natural disasters such as floods and forest fires,
- Leaks detection in municipal water distribution systems,
- Mapping noise levels in urban areas.
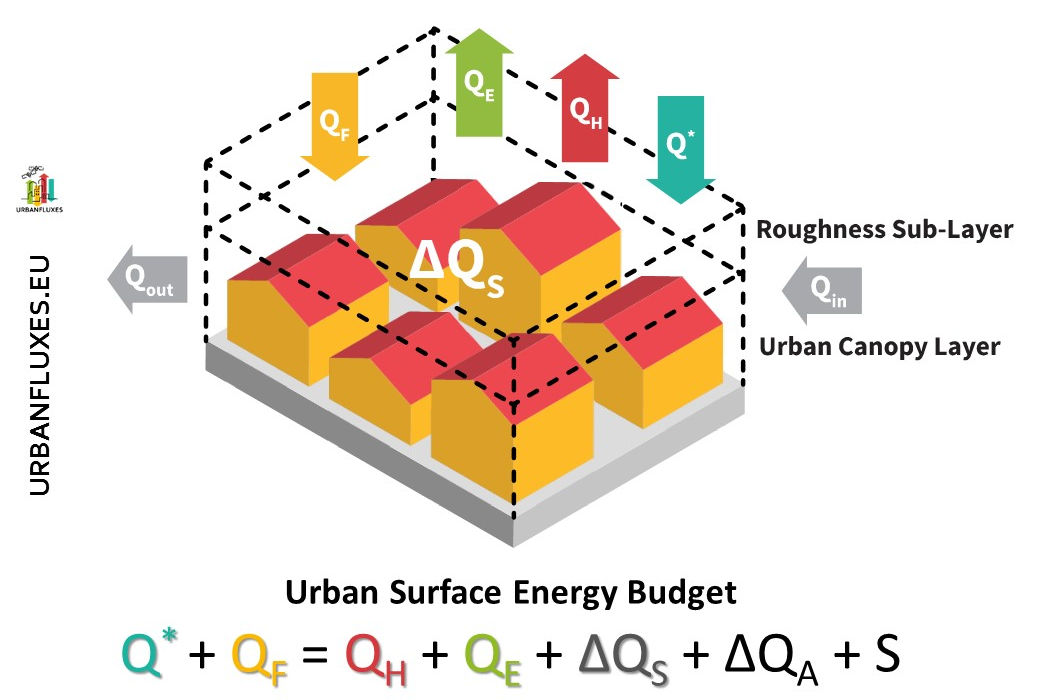
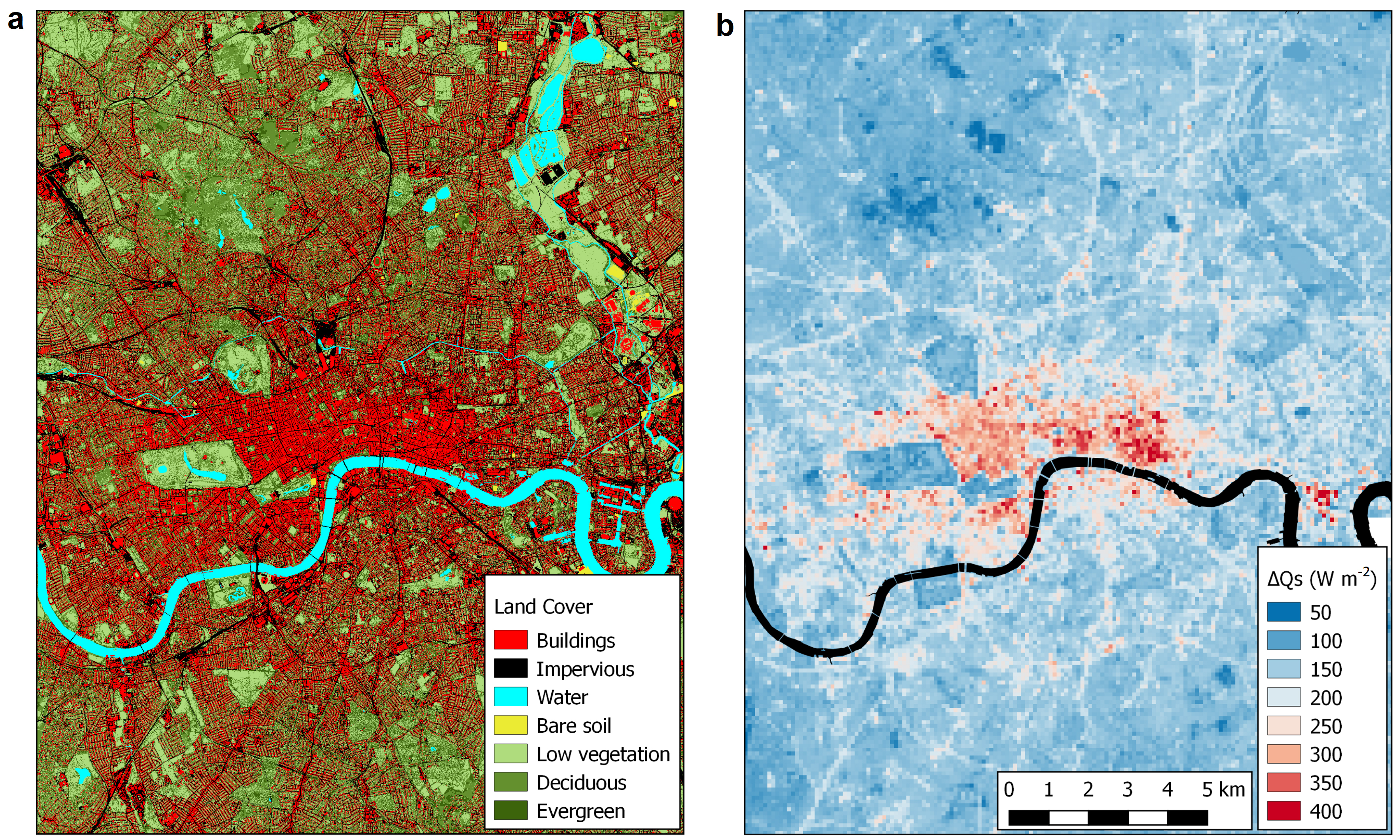
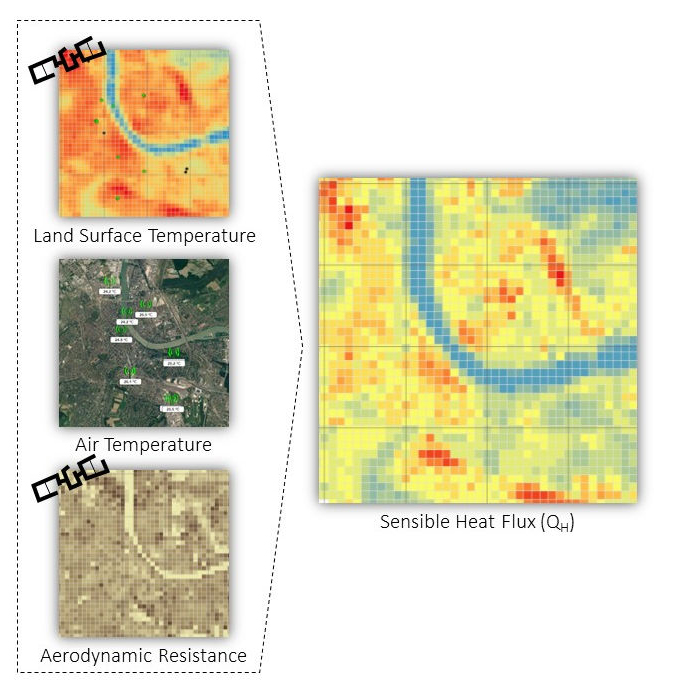
The Remote Sensing Laboratory: The Remote Sensing Laboratory (http://rslab.gr) concentrates in the field of Earth Observation (EO) and its area of research is the study of environmental phenomena and problems. The Lab operates a Wireless Sensors Network and a Micrometeorological Tower carrying Eddy Covariance and Net Radiation Infrastructures in the city of Heraklion. The Lab owns computational facilities and also it has access to cloud computing Infrastructures, such as Google Earth Engine and European Space Agency Urban-TEP, to analyze long time series of high spatial resolution satellite observations (Big Data). In the last ten years, the Lab has played a leading role in the domain of Urban Remote Sensing at European level, by coordinating relevant FP7, ERA.Net and H2020 projects, by publishing several articles in peer-review journals annually and by organizing and chairing Urban Remote Sensing sessions in the frame of big symposia, such as SPIE and JURSE. The focus of the activities of the Lab are on the analysis of both urban and natural environments.
- Concerning urban environment, the main focus is on urban climate and on urban planning, with emphasis on climate change mitigation and adaptation activities. More specifically, areas of research include the estimation of energy, water and carbon exchanges between the surface and the atmosphere. Several city typologies and climatically meaningful urban zoning systems are derived based on satellite observations. EO is used to monitor the dynamic changes of urban surface cover, fabric and morphology, providing quantitative estimates of relevant surface and atmospheric parameters, as well as, environmental indicators for supporting urban planning and management and assessing sustainability.
- Concerning natural environment, the Lab activities focus on environmental monitoring and development of methods for exploiting Earth Observation in improving future ecosystems, ecosystems services, as well as in supporting risk management for natural hazards.
Spatial spatiotemporal statistical modeling: The goal of spatial/spatiotemporal statistical modeling is to analyze datasets with spatial/spatiotemporal information to identify the underlying relationships and patterns and to compute predictions of unknown quantities in space and time. Bayesian space-time models, spatial econometrics, eigenvector filtering, and multivariate analysis are some of the techniques used. Areas of applications include:
- Short-term traffic forecasting and incident detection,
- Epidemiology,
- Analysis of environmental data,
- Geodemography,
- Regional economics.
Spatial Analysis
Geographic Information Systems & Remote Sensing.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMS
A. ONGOING PROJECTS
- CLMS-Cities: Improve the Copernicus Land Monitoring Servive (CLMS) with new elements and products, capable of being integrated into land planning decisions with regards to climate change mitigation and adaptation at local scale, across European cities.
Funding Agency: Horizon EUROPE
Duration: 2025-2028. - C-BLUES: Carbon sequestration in blue ecosystems
Funding Agency: Horizon EUROPE
Duration: 2024-2028. - UpClim: Upgrading a climate model to improve regional climate projections
Funding Agency: Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (H.F.R.I.)
Duration: 2024-2025 - URBISPHERE: Synergy Project funded by the European Research Council (ERC-SyG) that focuses on understanding, forecasting, and projecting feedbacks between climate change and drivers of urban transformation, and aims to change how the scientific community conceptualises, classifies and predicts the climate system and urban planning.
Duration: 2020-2026 - HARMONIA: EU-funded H2020 project that leverages existing tools, services and novel technologies to develop a platform supporting local policy-makers and citizens to understand the effects of Climate Change, and providing actionable data for smarter development strategies as well as generating opportunities for business growth and urban sustainability.
Duration: 2021-2025
B. COMPLETED PROJECTS
- LIFE IGIC: The Life IGIC project will develop Green Infrastructure (GI) and supporting Sustainable Farming Methods in pilot olive orchards, in Western Messara plain, south Crete, Greece.
Duration: 2017-2024 - CURE is an EU-funded H2020-Space project that synergistically exploits the Copernicus Core Services and develops a system for urban resilience in DIAS (Data and Information Access Services), consisting of cross-cutting applications for climate change adaptation/mitigation, energy and economy, as well as healthy cities and social environments, concerning several European cities.
Duration: 2020-2022 - POLITEIA II: Cultural Heritage - Technology (2017-2020). POLITEIA ΙΙ is an integrated interdisciplinary research action for the development and the best use of innovative technologies in the domain of Cultural Heritage.
- PERAN: Innovative research actions for environmental research and development (2017-2020). PERAN is a research program on environmental issues in which all FORTHs institutes are participating.
- EPIRROH: Information system for monitoring the leaks in municipal water systems (2017-2019). The objective of the project is the development of an information system for monitoring the Municipal Water Supply Network Monitoring System.
- THINKNATURE: EU-funded H2020 project ThinkNature is developing of a multi-stakeholder communication platform that will support the understanding and the promotion of nature based solutions in local, regional, EU and International level.
- SEN4RUS: The ERA.Net-RUS Plus project SEN4RUS (exploiting Sentinels for supporting urban planning applications at city and regional levels in Russia) aims at taking into account the specific requirements of spatial and urban planning in Russia to develop indicators that effectively and efficiently exploit the information content provided by Copernicus Sentinels mass data streams in support of city and regional planning.
- FLIRE: The EU-funded LIFE+ project Floods and Fire risk assessment and management was a demonstration project aiming to the development of an integrated Web-based Decision Support System (DSS) for both flash floods and forest fires risk assessment and management.
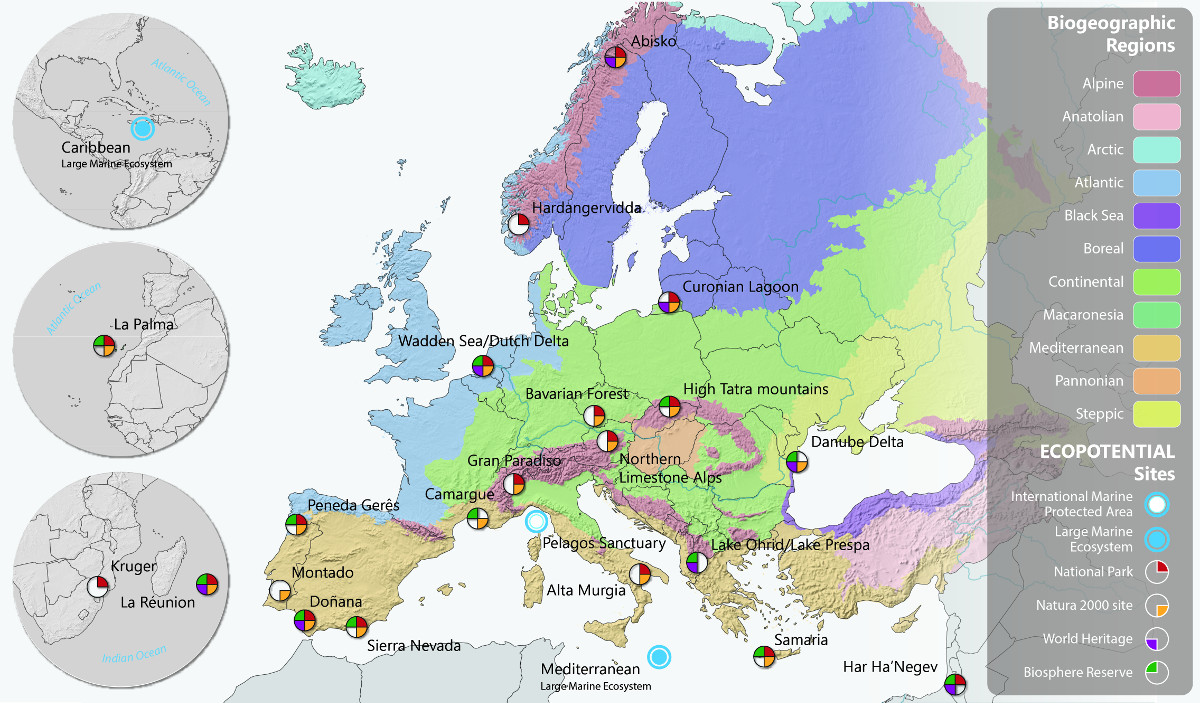
- ECOPOTENTIAL: The EU-funded H2020 Improving future Εcosystem benefits through Earth Observations is a large project that focuses its activities on a targeted set of internationally recognised Protected Areas, blending Earth Observations from remote sensing and field measurements, data analysis and modelling of current and future ecosystem conditions and services.
- GEOURBAN: The ERA.Net-RUS project Earth Observation in sUstainable uRBan plAnning & maNagement aimed to bridge the gap between EO scientists and urban planners by demonstrating the ability of current and future EO systems to depict parameters of urban structure and urban environmental quality over large areas at detailed level.
- URBANFLUXES: URBan ANthrpogenic heat FLUX from Earth observation Satellites (2015-2017). EU-funded H2020 URBan ANthropogenic heat FLUX from Earth observation Satellites is a Space project on “New ideas for Earth-relevant space applications” aims to investigate the potential of Earth Observation (EO) to retrieve anthropogenic heat fluxes.
- PROgRESSIon: PRotOtyping the Retrievals of Energy fluxes and Soil Surface moIsture (2011-2013). Understanding Earth system natural processes, as well as the interactions of Earth system components with anthropogenic activities - particularly so in the context of global climate change - has been recognised by the global scientific community as a very urgent and important research direction requiring attention for further investigation.
- BRIDGE: The EU-funded FP7 sustainaBle uRban plannIng Decision support accountinG for urban mEtabolism aimed at bridging the gap between bio-physical sciences and urban planners and to illustrate the advantages of accounting for environmental issues on a routine basis in design decisions.
- TAHOMA: Earth Observation for Surface Energy Balance) was a bilateral collaboration between Greece and France, aimed at reviewing existing (Earth Observation) EO systems and state-of-the-art methods to identify their capabilities and limitations in supporting Surface Energy Balance (SEB) modelling.
- PW: Precipitable Water was a bilateral collaboration between Greece and China, aimed at providing accurate precipitable water spatial distribution maps over Greece, capable of being used in regional and local studies.
PUBLICATIONS
-
2026
- A Arias-Ortiz, A Lafratta, P Colarusso, J Fourqurean, C Fu, H Kennedy, J Krause, P Lavery, C Leiva-Dueñas, N Marba, M Mateo, I Mazarrasa, D Poursanidis, C Salinas, O Serrano, M Stankovic, N Piñeiro, A Werner, M Wesselmann, CM Duarte, J Garcia-Orellana, P Masque (2026) Seagrass sediment organic carbon burial rates are globally significant, Springer Science and Business Media LLC, (pdf file)
- A Arias-Ortiz, D Poursanidis, IE Hendriks, J Mañez, K Hancke, C Lindemann (2026) Mapping, Monitoring, and Modeling Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Fluxes in Coastal Habitats to Advance Blue Carbon Science II Oral, AGU 2026 Ocean Sciences Meeting
- BFR Davies, S Oiry, M Roca, P Rosa, ML Zoffoli, D Poursanidis, T Dolch, B Ondiviela, C Galván, AC Brito, RJ Lilley, LL Govers, M Gade, L Barillé, P Gernez (2026) An initial map of European intertidal seagrass, Remote Sensing of Environment 333, 115116, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2025.115116
- IE Hendriks, AA Ortiz, D Poursanidis, J Mañez, S Comeau (2026) Mapping, Monitoring, and Modeling Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Fluxes in Coastal Habitats to Advance Blue Carbon Science I Oral, AGU 2026 Ocean Sciences Meeting
- C Lindemann, CP Lavin, D Poursanidis, S Comeau, H Gundersen, IE Hendriks, SC Lee, C Miller, AA Ortiz, KOzkan, K Hancke (2026) Remote sensing and in situ methods for assessing blue carbon ecosystems, 2026 Ocean Sciences Meeting
- K von Schuckmann, A Godoy-Faundez, V Garçon, FE Muller-Karger, K Evans, W Appeltans, N Bax, L Benedetti Cecchi, A Bernard, K Bernard, J Byrnes, G Canonico, L Chapuis, MR Clark, AM Darnaude, C Davies, P Englyst, A Fransson, S Hallam, E Heslop, E Holland, M Hood, S Kern, A Liné, A Lara-Lopez, N Loose, BM Míguez, CR McMahon, LM Nordlund, J Post, S Speich, A Sutton, T Tanhua, M Telszewski, D Poursanidis, W Yu (2026) Global ocean indicators: Marking pathways at the science-policy nexus, Marine Policy 184, 106922, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpol.2025.106922
- 2025
- 2024
- 2023
- 2022
- 2021
- 2020
- 2019
- 2018
- 2017
- 2016
- 2015
- 2014
- 2013
PEOPLE
RESEARCHERS
- Prastacos, Poulicos, Collaborating Researcher, Former Research Director
- Chrysoulakis, Nektarios, Research Director
- Doxa, Aggeliki, Assistant Professor, University of Crete
- Kamarianakis, Yiannis, Research Director
- Mitraka, Zina, Principal Researcher
TECHNICAL SCIENTISTS
- Manioudakis, Nikos, Technical Scientist
- Poursanidis, Dimitris, Technical Scientist
CONTACT US
For any information regarding the group please contact:
Spatial Analysis Group,
Institute of Applied and Computational Mathematics,
Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas
Nikolaou Plastira 100, Vassilika Vouton,
GR 700 13 Heraklion, Crete
GREECE
Tel: +30 2810 391800
E-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. (Mrs. Maria Papadaki)
Tel.: +30 2810 391805
E-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. (Yiota Rigopoulou)
Spatial Analysis Group,
Institute of Applied and Computational Mathematics,
Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas
Nikolaou Plastira 100, Vassilika Vouton,
GR 700 13 Heraklion, Crete
GREECE
Tel: +30 2810 391800
E-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. (Mrs. Maria Papadaki)
Tel.: +30 2810 391805
E-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. (Yiota Rigopoulou)